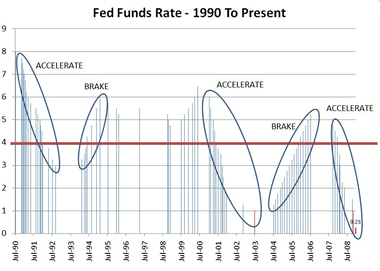
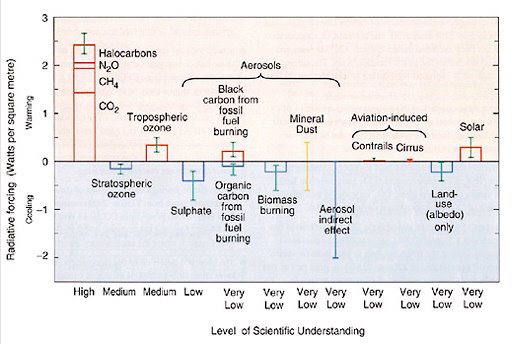
Energy Wise?
SEARCH BLOG: AUTOMOBILE
A couple of energy-related items caught my eye today. Somehow, I don't see the answers here.
Fuel economy debate heats up
Automakers call claims misleadingNone of these cars actually average 43 mpg:
May 30, 2007
BY JUSTIN HYDE
FREE PRESS WASHINGTON STAFF
WASHINGTON -- In an escalation of a war of words, automakers accused California regulators on Tuesday of misleading federal officials and the public about the costs and benefits of California's proposed 30% cut in global warming emissions from cars and trucks.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is considering whether to grant California's request for a waiver allowing its rules, which would force automakers to improve the mileage of their vehicles to roughly 43 m.p.g. by 2016 [8 MODEL YEARS]. The waiver also would apply to 11 other states that have adopted California's standards; another seven states are debating them.
40 - 49 mpg [highway] cars [source]
I guess we will have to be driving even smaller cars....

Cheaper form of ethanol on the way
MSU prof predicts viable fuel choiceLet's see... Texas alone uses 250 million barrels of gasoline per year. What's the likelihood that we can produce even close to a billion barrels of cellulosic ethanol? Eh, slim?
May 30, 2007
BY KATIE MERX
FREE PRESS BUSINESS WRITER
Ethanol could become a more practical fuel for Americans who would like to slow the pace of global warming and their dependence on foreign oil, if one Michigan State University professor's predictions about ethanol production are accurate.
MSU professor Bruce Dale says the cost of so-called cellulosic ethanol -- a form of ethanol produced from nonfood plant materials -- could be cut in half, to about $1.30 per gallon by 2012, and fall below $1 per gallon by 2020. Dale said it costs about $2.20 per gallon to produce gasoline at current oil prices.
"By 2020 we will be producing tens of billions of gallons of cellulosic ethanol per year for much less than $1 per gallon," said Dale, who has been working for more than 30 years on ways to turn plant cellulose into ethanol for fuel. There would still be a markup at the pump, but he says the lower production cost could make ethanol not only a viable alternative to gasoline, but a less-expensive alternative, even on a per-mile basis.
..